CocosCreator中使用pureMvc
PureMVC框架的目标很明确,即把程序分为低耦合的三层:Model、View和Controller。
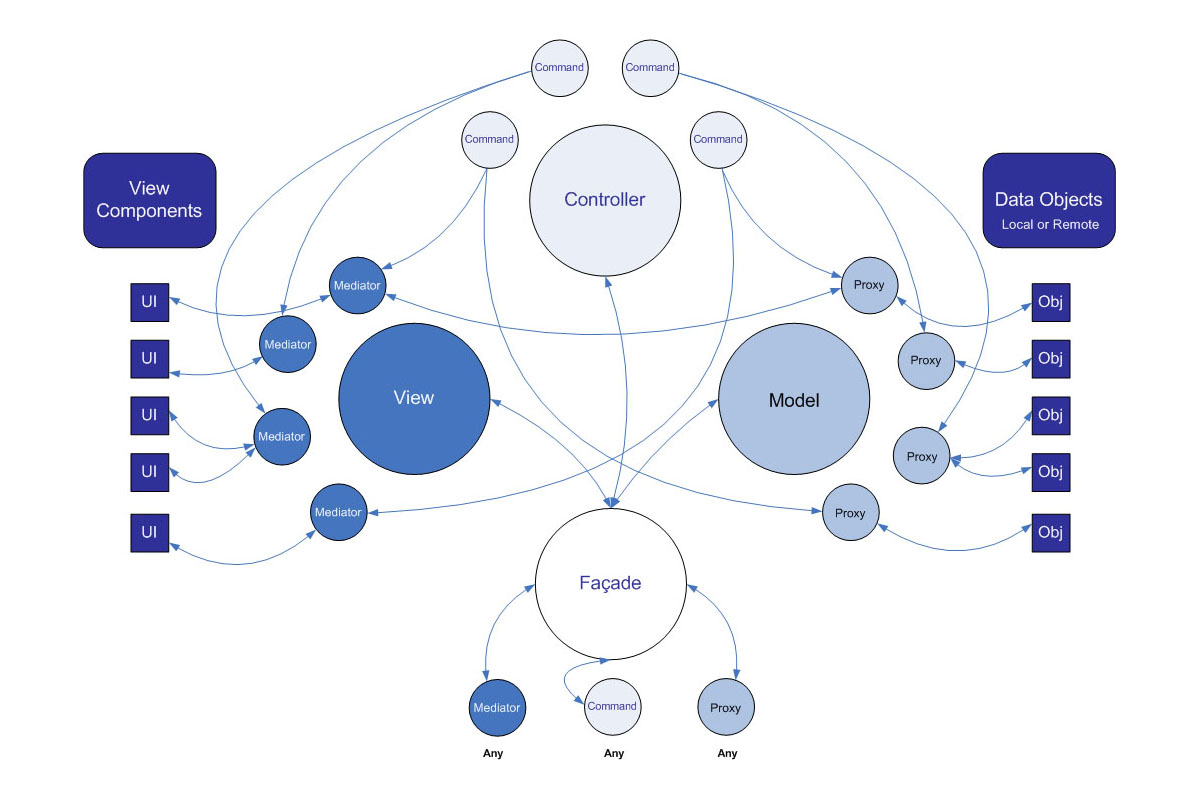
PureMvc的结构
Model与Proxy
Model保存对Proxy对象的引用,Proxy负责操作数据模型,与远程服务器通信存取数据
View与Mediator
View保存对Mediator对象的引用,由Mediator对象来操作具体的视图组件(ViewComponent, 在ccc中即为继承自cc.Component的各种UI组件),包括添加事件监听器,发送或者接受Notification,直接改变视图的状态
改变视图状态要在Mediator实现,也可以在ViewComponent中即继承自cc.Component的组件脚步中实现修改视图的API在Mediator中调用
Controller与Command
Controller保存所有Command的映射,Command类是无状态,只有在需要的时候才被创建。Command可以获取Proxy对象并与之交互,发送Notification,执行其他的Command。
Facade与Core
Facade类使用单例模式,他负责初始化核心层(Model, View和Controller),可以访问他们的Public方法
实际的应用中,只要继承Facade类创建一个具体的Facade就可以实现整个MVC的模式,不需要在代码中导入编写Model,View和Controller类
Proxy,Mediator和Command就可以通过创建的Facade类来相互访问通信
Notification可以被用来触发Command的执行
Facade保存了Command与Notification之间的映射。当Notification(通知)被发出的时候,对应的Command(命令)就会自动的由Controller执行。Command实现复杂的交互,降低View和Model的耦合度
Mediator发送 声明 接收Notification
当用View注册Mediator时,Mediator的listNotification方法会被调用,以数组的形式返回该Mediator对象所关心的所有Notification,之后当系统其他角色发出同名的Notification(通知)的时候,关心这个通知的Mediator都会调用handleNotification方法并将Notification以参数的形式传递到方法
我可以在多个Mediator中注册相同的Notification,当系统其他角色发送Notification的时候,我注册的多个Mediator都能收到,广播和收音机的关系
Proxy只发送,不接收Notification
在很多场景下Proxy需要发送Notification(通知),比如:Proxy从远程服务器接收到数据时,发送Notification告诉系统,或当Proxy的数据被更新的时候,发送Notification告诉系统
如果让Proxy也监听Notification(通知)会导致它和View(视图)层和Controller(控制)层的耦合度太高
View和Controller必须监听Proxy发送的Notification,因为他们的职责就是通过可视化的界面使用户能与Proxy持有的数据交互
不过对View层和Controller层的改变不应该影响到Model层
MVC元设计模式的核心要素在purMvc中体现为Model类,View类和Controller类。为了简化程序开发,pureMvc应用了Facade模式
Facade是Model,View和Controller三者的“经纪人”。实际编写代码的你不用导入这三者的类文件,也不直接使用他们。Facade类已经在构造方法包含了对核心MVC三者单例的构造
一般的,实际的应用程序都有一个Facade子类,这个Facade类对象负责初始化Controller(控制器),建立Command与Notification名之间的映射,并执行一个Command注册所有的Model和View
Facade
- AppFacade需要继承Facade类并实现IFacade接口
- StartupCommand是一个启动的Command负责启动所有
- 在initializeController中注册了StartupCommand
- 在startup方法中发送系统通知STARTUP,然后就注销了StartupCommand(初始化只需要执行一次)
1 | |
Notification
pureMvc使用了观察者模式,所以各层之间能以一种松耦合的方式通信,并且与平台无关
Event与Notification
Facade和Proxy只能发送Notification,Mediators既可以发送也可以接受Notification,Notification被映射到Command,同时Command也可以发送Notification。这是一种”发布/订阅”机制,所有的观察者都可以收到相同的通知。例如多个收音机收到同一个FM调频,当有音乐播放时候,所有人都能听到。
定义Notification和Event的常量
公共的Notification名称常量很适合定义在Facade中,所有的Notification交互的参与者都是Facade的协作者
当这些Notification的名称常量需要被其他程序访问时,我们可以使用单独的“Constants”类来存放这些Notification名称常量定义。
不管什么时候都应该吧Notification名称定义为常量
Command
Facade实现类需要在启动时初始化Controller,建立Notification与Command的映射
Controller会注册监听每一个Notification,当被通知到时,Controller会实例化该Notification对应的Command类的对象。最后将Notification作为参数传递给execute方法
Command对象是无状态的,只有在需要的时候(Controller收到相应的Notification)才会被创建,并且在被执行(调用execute方法)之后就会被删除。所以不要在那些长生命周期的对象里面引用Command对象
Command是个短命鬼,生下来就为了爽一下,过把瘾就死
SimpleCommand和MacroCommand
Command要实现ICommand接口,在pureMvc中有两个类实现了ICommand接口,分别是SimpleCommand和MacroCommand
- SimpleCommand
SimpleCommand只有一个execute方法,execute方法接受一个INotification实例作为参数。实际应用中,你只需要重写这个方法就行了。
- MacroCommand
MacroCommand让你可以顺序执行多个Command。每个执行都会创建一个Command对象并传参一个对源Notification的引用
MacroCommand在构造方法调用自身的initializeMacroCommand方法。实际应用中,需要重写这个方法,调用addSubCommand添加子Command,可以随意组合SimpleCommand和MacroCommand成为一个新的Command
上文中的StartupCommand, 添加了3个初始化Command Proxy Mediator的Command
1 | |
上文中注册一个游戏Proxy的简单命令
1 | |
降低Command与Mediator Proxy的耦合度
通过发送Notification通知Controller来执行Command,而且只能由Controller实例化执行Command。
为了和系统其他部分交互与通信,Command可能需要
- 注册,删除 Mediator Proxy 和 Command,或者检查他们是否已经注册
- 发送Notification通知Command或者Mediator做出响应
- 获取Proxy和Mediator对象并直接操作他们
Command使我们可以很容易的切换视图元素状态或者传送数据给它
Command可以调用多个Proxy执行事务处理,当事务结束后,发送Notification或者处理异常和失败
Command与Mediator和Proxy交互,应避免Mediator和Proxy直接交互
Mediator
Mediator是视图组件ViewComponent(在ccc中为继承cc.Component的UI控件脚本)交互的中间件
Mediator的职责
对基于pureMvc的应用程序来说,ViewComponent可以是任意的UIComponent,不用管所处的框架是什么,也不用管它有多少个组件。一个ViewComponent应该尽可能的把自己的状态和操作封装起来,只对外提供事件 方法和属性的简单API
Mediator保存了一个或者多个ViewComponent的引用,通过ViewComponent自身提供的API管理他们
Mediator的主要职责是处理ViewComponent派发的事件和系统其他部分发出来的Notification
因为Mediator也会经常和Proxy交互,所以经常在Mediator的构造方法中取得Proxy实例的引用并保存在Mediator的属性中,这样避免频繁的获取Proxy实例
Mediator负责处理与Controller层 Model层交互,在收到相关的Notification的时候更新ViewComponet
一个Mediator的事件响应会有以下几种处理
- 检查事件类型或者事件的自定义内容
- 检查或者修改ViewComponent的属性或者提供的方法
- 检查或者修改Proxy对象的属性或者提供的方法
- 发送一个或者多个Notification, 通知别的Mediator或者Command做出反应(甚至可以发送给本人)
小Tips:
- 如果多个Mediator对同一个事件做出响应,那么应该发送应该Notification,然后相关的Mediator做出各自的响应
- 如果应该Mediator需要和其他Mediator进行大量的交互,那么应该好方法是利益Command吧交互步骤定义在一个地方
- 不应该让一个Mediator直接去获取调用其他的Mediator,在Mediator中定义这样的操作本身是错误的
- Proxy是有状态的,当状态发送变化时发送Notification通知Mediator,将数据的变化反映到视图
在Mediator中处理Notification
在Mediator实例化时,pureMvc会调用Mediator的listNotificationInterests方法查询关心的Notification,Mediator则在listNotificationInterests方法中以数据的形式返回这些Notification的名称。
当这个数组例的一个Notification被系统的其他部分发出时,Mediator对象的handleNotification函数会被调用,并传入Notification参数
Mediator和Proxy之间 Mediator和其他Mediator之间的耦合
View本质上是显示Model的数据让用户能与之交互,我们期望一种单向依赖,即View依赖于Model,而Model却不依赖于View。View必须知道Model的数据是什么,但是Model却并不需要知道View的任何内容
虽然Mediator可以任意访问Proxy,通过Proxy的API读取 操作Data Object,但是,由Command来做这些工作可以实现View和Model之间的松耦合
如果一个Mediator有太多的Proxy及其他数据的操作,那么应该把这些代码重构在Command内,简化Mediator,把业务逻辑放到Command上,这样Command可以被View的其他部分重用,还会实现View和Model之间的松耦合提高扩展性
用户与ViewComponent和Mediator的交互
- 构建值对象用来作为Notification的参数传递
- Mediator收到的Notification包含Proxy处理的值对象
Proxy
一个Proxy有可能管理对本地创建的数据结构的访问。它是Proxy的数据对象。
RemoteProxy被用来封装与远程的数据访问。Proxy维护那些与RemoteService通信的对象,并控制对这些数据的访问。
在这种情况下,调用Proxy获取数据的方法,然后等待Proxy在收到远程服务的数据后发出异步Notification
Proxy的职责
Proxy封装了数据模型,管理Data Object及对Data Object的访问,不管数据来自哪里,什么类型
在pureMvc中,Proxy是个被Model注册的简单的数据持有者
虽然Proxy类已经是完全可用的了,但是通常对于具体的应用你应该编写Proxy的子类,增加操作方法
一般的Proxy有下面几种类型
- Remote Proxy 当Proxy管理的数据存放在远程终端,通过某种服务访问
- Proxy and Delegate,多个Proxy共享对应该服务的访问,由Delegate封装对服务的控制访问,确保响应正确的返回给相应的请求者
- Protection Proxy 用于数据对象的访问有不同的权限时
- Virtual Proxy 对创建开销很的数据对象进行管理
- Smart Proxy首次访问时载入对象到内容,并计算它被引用的次数,允许锁定确保其他对象不能修改
避免对Mediator的依赖
Proxy不监听Notification,也永远不会被通知,因为Proxy并不关心View的状态。但是,Proxy提供的方法和属性让其他角色关心数据
Proxy对象不应该通过引用 操作 Mediator对象来通知系统它的DataObject发生了改变
使用Notification的方式,把Model层和系统操作隔离开来,这样View层和Controller层被重构时不会影响到Model层
但是反过来就不是这样了, Model层的改变很难不影响到View层和Controller层。毕竟,他们存在的目的就是让用户与Model层交互的
封装域逻辑
Model层中的改变总会造成View/Controller层的一些重构
我们把Domain Logic 尽可能放在Proxy中实现,这样尽可能做到Model层与相关联的View层 Controller层的分离
域逻辑?????
Proxy不仅仅用来管理数据对象的访问,而且用来封装数据对象的操作使数据维持在一个合法的状态
比如计算营业税是一个Domain Logic,它应该放在Proxy中实现而不是Mediator或Command
与Remote Proxy通信
Remote Proxy对象是一个从远程位置获取DataObject的Proxy。这通常意味着我们与它的交互是以异步的方式
调用远程服务的查询并返回的结果,这个过程通常有以下几步
- 一个ViewComponent触发一个事件,发起一个请求
- 它的Mediator相应,获取相应的RemoteProxy设置它的查询内容
- Proxy的通过内部的HttpService初始化查询请求
- 当服务器返回结果时,HttpService会触发回调,Proxy响应回调
- Proxy发送一个Notification表示请求成功,并把结果封装成值对象传递
- 关心这个Notification的Mediator就会响应这个Notification并获得封装的值对象
- 然后通过Mediator刷新View
pureMvc官网的PDF
pureMvc与CocosCreator的demo

代码的目录结构
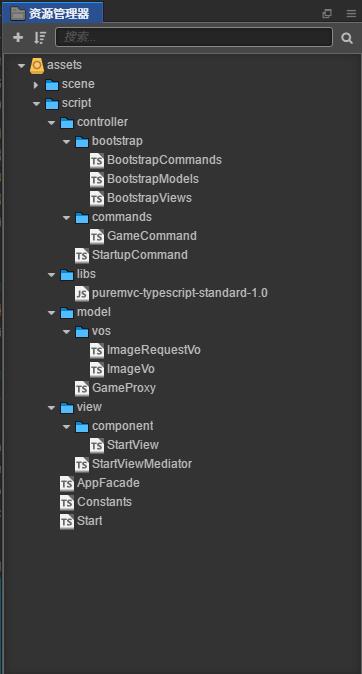
Start
- 用来启动pureMvc的地方
1 | |
Constans
- 用来保存图片下载结果Notification常量的地方
1 | |
StartViewMediator
- listNotificationInterests表示要关心的Notification
- handleNotification是处理Notification的地方
- onRegister中加入了按钮的监听
- 构建了一个ImageRequestVo的值对象用来传递需要下载的图片信息
- 使用sendNotification发送下载消息给Command(如果直接使用Proxy会增加耦合)
1 | |
StartView
- CocosCreator中的脚步(作为当前系统下的ViewComponent)
- 根据生命周期加入了注册和移除Mediator的方法
- 暴露了setSprite的方法可以修改图片
1 | |
GameProxy
- NAME命名当前的Proxy
- fetchTest执行当前的下载图片的操作
- 在异步下载完成后使用sendNotification发送结果给系统
1 | |
ImageVo
- 值对象
1 | |
ImageRequestVo
- 值对象
1 | |
StartupCommand
- 启动初始化的Command
- 加了多个子Command
1 | |
GameCommand
- 执行下载图片操作的Command
- 通过execute方法调用Proxy执行下载操作
1 | |
BootstrapViews
- 初始化需要用到的view的Command
1 | |
BootstrapModels
- 初始化需要用到的Proxy的Command
1 | |
BootstrapCommands
- 初始化需要用到的Command的Command
1 | |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!